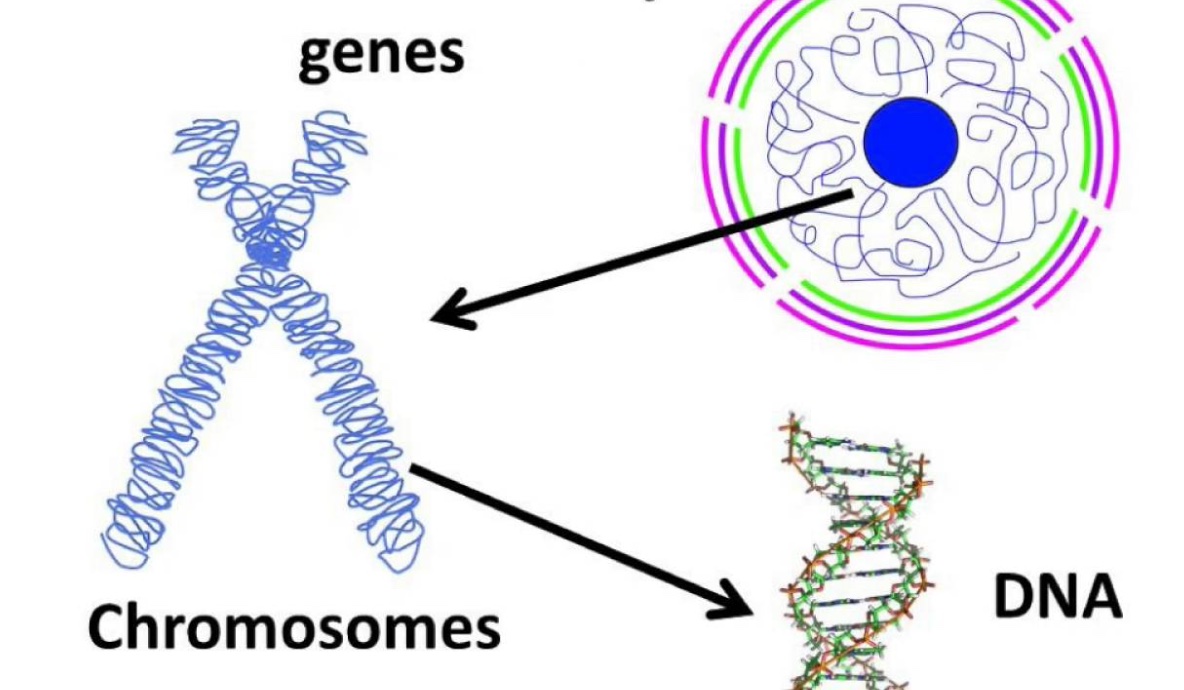
DNA, Chromosomes, and Genes – The Building Blocks Of The Genetic Code
LAST UPDATED: November 10, 2022
In the era of making reels, people have been mixing everything, whether or not it makes any sense. But what makes sense is you and your cousin look the same or have habits that may be the same. This can seem a little tricky to understand. Come, let’s talk about this in detail
Have you come to a time when you don’t know what to do in certain situations or how to handle them? And you go to your parents or siblings for assistance? Why is it that the first thought that comes to our mind when we find ourselves in trouble is of our blood relatives? This is because we share a certain relationship with them that links us to them and makes us feel close to them.
You may also come across situations where you grow up; you are referred to as Junior Billy, Junior Mary, or whatever your parents’ names are, but your sibling may not be called the same. Do you ever wonder why? It’s not that every sibling may be the exact replica of each other when it comes to talking to elders or interacting with others. Some may be introverts, and some may be shy, while others may be outgoing. The reason is that you inherited traits from both your mother and father. But the amount or percentage may vary and is not the same.
We are pretty sure you must be aware of the terms DNA, chromosomes, and genes. If you don’t hold extensive knowledge about these topics, we are here to guide you through them. So, let’s begin –
DNA
DNA as we know it, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a hereditary material present in humans as well as other organisms. It is seen that almost every person’s body inherits the same DNA. While some amount of DNA is found in the mitochondria, most of the DNA is located in the cell nucleus. DNA is responsible for supplying the genetic instructions that focus on telling living creatures how to develop, live, and reproduce.
A single DNA molecule is made with two strands wound around each other. DNA is passed on from parents, both mother, and father, to their child. The amount (or percentage) of DNA passes may vary with each individual. For instance, A may have 40% of the mother’s DNA and 60% of the father’s, whereas B may have 70% of the mother’s DNA and only 30% of the father’s. But what’s certain is they both will have a mixture of both, which makes it understandable why you have a nose like your father and hair like your mother.
Siblings may also share the same habits or looks because of their common source of DNA. Whether or not in the same proportion, siblings are likely to share traits in different ways.
Now, let’s have a look at the facts about DNA –
- DNA is made up of four bases – Guanine, Adenine, Thymine, and Cytosine. Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Guanine pairs with Cytosine when forming a DNA.
- In our genome, there are around 3 million DNA bases present.
- A DNA test may bring light to your risk of genetic diseases and make you precautious about it beforehand.
- Whether plant, animal, or human being, DNA is found in every living thing.
- We share 9% of our DNA with other human beings.
Wow. This makes us understand why we share certain habits or looks with our parents or blood relatives.
Chromosomes
Now, as we’re quite aware of the term DNA, chromosomes may sound like brand new information to some of us. But don’t worry, we will help you with this and make you well versed in it.
First things first, it may sound like a nutcracker to spell, but it’s not that difficult. A chromosome is pronounced as KROH-muh-some, meaning a structure that is found inside the nucleus of a cell. A chromosome consists of proteins and DNA organized into genes.
Normally, each cell consists of about 23 pairs of chromosomes. A chromosome is not visible in the cell’s nucleus, not even with the help of a microscope. But, chromosomes become tightly packed during cell division which makes them visible under a microscope.
Each chromosome is divided into two sections with a constriction point called the centromere. The two sections called arms are labeled as “p arm,” the short arm of the chromosome, and “q arm,” the long arm of the chromosome.
Now, let’s have a look at the facts about chromosomes –
- The number of chromosomes varies in each organism across different species.
- The gender is decided by the chromosomes. While a human male consists of the X chromosome and the Y chromosome, a female human consists of only an X chromosome.
- X+X = Female
- X+Y = Male
- The size of the Y chromosome is about one-third the size of the X chromosome.
- Histones are spool-like proteins that keep the DNA tightly wrapped in the unique structure of chromosomes.
We hope this made you learn a little more about chromosomes. Did you also know the term Chromosome comes from the Greek words chroma meaning color, and soma, meaning body?
Genes
Genes are made up of DNA. In the human body, genes vary from a few hundred DNA to around 2 million bases (or more). Each individual possesses two copies of each gene, one inherited from each parent. A gene is basically the unit of heredity passed from parent to their children. They contain information that makes specific proteins lead to the expression of a specific physical trait or characteristic – like the texture of your hair, eye color, or any other particular function in a cell.
Almost everything about a living being is decided by genes. Hundreds of internal and external factors might get affected by genes. The reason behind having height like your father or eyes like your mother is because of genes. Genes come from our parents, making us look and behave like this in a certain manner.
In 1990, the Human Genome Project was started at the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Department of Energy by a group of international researchers. Their aim was to sequence 3 billion base pairs in the human genome. The project came to an end in the year 2003, which leaves us with access to the data generated during the tenure.
Now let’s dive into some facts about Genes!
- Almost 99% of the genes are exactly the same in each human being. This makes us humans 99% identical on a genetic level. Wow, that was something new!
- The primary purpose of genes is to store information.
- Genes collectively are called alleles which come in different forms.
- Identical twins have the same genetic code, but their development may be influenced by various other factors.
Those were some interesting facts. This is the very reason why some kids have talents like rolling their tongue or folding their ears entirely because their parents inherit these qualities.
Now let’s have a sneak-peek into Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms, what they are, and what their importance is. Come, let’s find out –
A Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms or SNP (pronounced as snip) is basically the most common type of genetic variation among people. In the DNA sequence, if 1% of the population does not carry the same nucleotide at a particular position, then this variation is classified as SNP. When an SNP occurs in a gene, it is said to have two or more alleles.
Genetic Code
While DNA, chromosomes, and genes are the building blocks of genetic code, what is genetic code?
A code that our body uses to convert instructions present in our DNA is called a genetic code. The genetic code was believed to be identical in all forms of life, but recent studies show that they differ in certain organisms. Genetic code has a universal nature, meaning all species (with minor exceptions) use it for protein synthesis.
For a better understanding of the genetic code, here are a few of its characteristics –
- All organisms share a common evolutionary history as they all have the same genetic code.
- Everything in our cells, from hereditary information to various traits, is ultimately built and based on the genetic code.
- Mutations are changes in the genetic sequence that may be the main cause of variation among organisms.
Now, after reading all about DNA, chromosomes, and genes, you must be thinking about how they are related to each other. Let’s have a look at how DNA, chromosomes, and genes are related to each other with an easy example –
Let’s use the analogy of a city to get a better understanding of the relation between the three mentioned terms. One DNA would be represented as one house on the street, a gene would be represented by an entire street of houses, and a chromosome would be implied as all the streets in a neighborhood. In other words, DNA molecules, when combined, form a chromosome, and each chromosome consists of multiple genes.
After having read about DNA, chromosomes, and genes, it has become clear that all these terms are interrelated to each other and help in deciding the behavior of a human body. Whether tall, short, fair, or skinny, each quality you possess is passed on by your parents. But if this is the case, why do siblings fight? 😛 It’s because every individual has certain traits making them unique from others.
We think you are now ready to flaunt your knowledge about DNA, genes, and chromosomes to your friends and family. Let them know the scientific reason behind the shared traits in the family.
We hope you had a great time indulging and reading our blog. A scientific topic can be dull, but we enjoyed writing it for you as simplified as possible.
Happy Reading Y’all! We would be pleased to see you again on our page!
